5.1 High-Resolution Core Photography and Spectral Gamma-Ray Logging
5.1.1 Introduction
A key element for potential production from Upper Ordovician shales, as with any shale play, is TOC. High-resolution photography and spectral gamma-ray (SGR) core logging not only facilitates core descriptions but also provides an opportunity to link wireline log data to rock analytical data such as TOC.
Using this approach may help identify a proxy for predicting TOC and/or better constrain chronologic stratigraphy.
The method of using GR, SGR and density data as proxies for TOC has been performed for other shales in the Appalachian basin (including the Marcellus Shale), and in other basins such as the Alberta of Western Canada (Lunig and Kolonic, 2003).
5.1.2 Materials and Methods
As team lead for this particular task, ODGS reviewed available data on the Upper Ordovician section in Ohio, including core, rock cuttings, paper geophysical logs, LAS files and source rock analyses.
ODGS recorded 761 cutting suites, 193 wells with TOC analyses, 68 wells with downhole SGR logs, 58 wells with LAS files and 48 cores.
A series of location maps was generated for each data type to determine its geographic coverage across the state.
We used these maps to determine where additional data needed to be collected to augment the existing dataset for this task.
Although cuttings samples were available from 761 wells, once the availability of preferred logs (i.e., GR, SGR and density run post-1990) was taken into consideration, only cuttings from 15 wells were chosen for TOC analysis.
In addition, three rock cores were chosen for analysis.
Data from these 18 well locations were added to the legacy database that contained TOC data for 193 wells, resulting in a TOC data count of 211 Ohio wells.
Combining these data with data from wells in other states, and additional data that became public during the term of the Study, resulted in a grand total of 382 wells with TOC data.
Core sampling was imperative for this work because it provided the most accurate depth values for TOC analysis to incorporate into LAS logs.
The cores chosen by ODGS were strictly based on geographic location, additional available data and overall condition, with little priority given to age and/or availability of modern logs because the core could be scanned as part of the present work.
Prior to any sampling or scanning, high-resolution photographs were taken using a Nikon D700 camera.
This provided a permanent visual record of the core in its initial condition.
Each photo image file was named based on the core footage, box number and whether the core was wet or dry.
Once a core had been photographed and archived, it was scanned using the Core Lab SGL-300 Spectral Gamma Logger (SGL-300).
The SGL-300 is owned by The Ohio State University’s Subsurface Energy Materials Characterization & Analysis Laboratory (SEMCAL) and is housed at the ODGS Horace R. Collins Laboratory (HRC).
It scans core at high resolution and creates LAS geophysical logs of GR, uranium-free gamma-ray (UFREE and KTh), potassium (POTA), uranium (URAN), thorium (THOR) and bulk density (RHOB).
These logs allow geologists to accurately correlate core with other physical data.
The SGL-300 is calibrated daily to a set of standards to ensure the production of accurate and consistent data that can be directly compared to all other core scans.
Core is scanned continuously from bottom to top at a rate of 6 in per minute when gathering SGR data and 3 in per minute when measuring RHOB.
Information for each data type is recorded every inch, but in order for the SGL to create a "geophysical log-like curve", each data point is based on a progressing average of the previous 6 in of scanned core.
In a single day, the maximum length of core that can be scanned is either 300 ft for SGR or 150 ft for RHOB.
Cores in excess of these lengths require multiple days of scanning, which also requires recalibration and stitching together numerous LAS output files.
To accommodate a seamless LAS merge, each subsequent scan began by rescanning the last 10 ft of core from the previous day.
A total of 14 cores (eight from Ohio, three from West Virginia, two from Kentucky and one from New York) were photographed, scanned and converted to LAS files.
No Pennsylvania core samples were available for this task.
To supplement the core scans, an additional 92 downhole geophysical logs were digitized using Neuralog software.
This provided a total of 162 LAS files, 124 of which include TOC data.
The TOC data were manually entered as a unique curve to each corresponding LAS file and were limited to wells that had 15 or more TOC data points.
When adding TOC data that originated from well cuttings to an LAS file, a midpoint of the cuttings sample interval was chosen as its corresponding depth.
However, TOC data derived from core could be added to the LAS file at their exact footage.
This combined dataset was imported into the Landmark GeoGraphix® software and displayed in crossplots for further analysis.
Correlations were made to analyze multiple aspects of the collected data, including which element is driving the overall radioactivity; how core SGR scans relate to downhole SGR;
if GR, POTA, URAN and/or THOR relate to TOC; and what, if any, relationships exist among different facies deposited during Lexington/Trenton-to-Point Pleasant time (Patchen and others, 2006).
We evaluated linear trends in data and refer to a correlation coefficient 'r'. These correlations are presented in the Section 5.1.5 below.
5.1.3 High-Resolution Core Photography
ODGS completed the task of taking high-resolution photographs of core from the Upper Ordovician interval (including Kope, Utica, Point Pleasant,
Upper Lexington/Trenton, Logana and Curdsville) in Ohio and equivalent core intervals from West Virginia, Kentucky and New York.
Photographs were taken using a ceiling-mounted, full-frame, Digital Single Lens Reflex (DSLR) camera with an Auto Focus AF-S 24 – 70mm f/2.8 G ED lens.
All photographs were exposed using color corrected 6000K light softboxes, creating consistent white balance. This consistency allows for a display of true colors that can be helpful when comparing core.
When possible, both wet and dry photographs were taken for each core box to capture better detail. Fourteen cores were photographed for this task (Table 5-1).
Core locations span approximately 600 miles (mi) across the Study area, from east-central Kentucky through Ohio, West Virginia and into central New York (Figure 5-1).
| Core # |
Name |
State |
County |
Footage |
Size (in) |
| 3446 |
Todhunter |
OH |
Butler |
27 – 381 |
2 ¼; Full Diameter |
| 860 |
V. Apple |
OH |
Butler |
67 – 693 |
2 ¼; Full Diameter/slabs |
| 2535 |
Howerton |
OH |
Clermont |
19 – 349 |
2 ¼; Full Diameter |
| 2536 |
Sky Valley RC |
OH |
Clermont |
21 – 319 |
2 ¼; Full Diameter |
| 3003 |
Fred T. Barth |
OH |
Coshocton |
5630 – 5749 |
3 ⅜; Full Diameter |
| 2626 |
J. Goins |
OH |
Highland |
600 – 1310 |
2 ¼; Full Diameter |
| 3372 |
Prudential |
OH |
Marion |
389 – 1604 |
2 ¼; Full Diameter |
| 3409 |
Aristech |
OH |
Scioto |
2734 – 3373 |
2 ¼; Full Diameter |
| 254 |
Lost River |
WV |
Hardy |
27 – 100 |
2 ¼; Full Diameter |
| 256 |
Lost River |
WV |
Hardy |
17 – 70 |
2 ¼; Full Diameter |
| 768 |
Power Oil |
WV |
Wood |
9417 – 9665 |
2 ¼; ⅓ Slab |
| 139 |
Bender CG&E |
KY |
Boone |
36 – 284 |
2 ¼; Full Diameter |
| 209 |
M. Burchell |
KY |
Montgomery |
20 – 904 |
2 ¼; Full Diameter |
| 74NY5 |
Mineral Core |
NY |
Herkimer |
21 – 763 |
2 ¼; ½ Slab |
Table 5-1. List of cores photographed and scanned with the SGL-300.
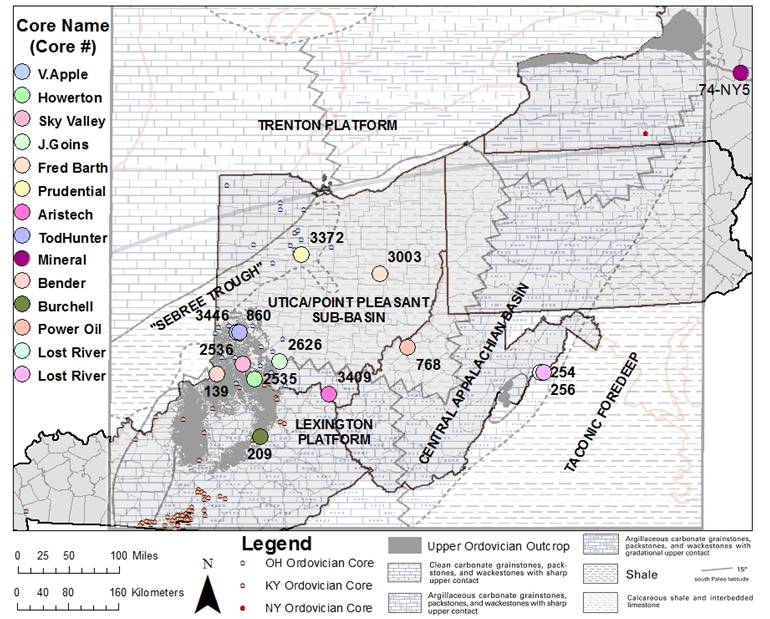
Figure 5-1. Regional map of Utica/Point Pleasant well locations for which cores were scanned and photographed. Facies map of Trenton/Point Pleasant time from Patchen and others (2006).
5.1.4 SGR Core Scan Results
5.1.4.1 Kentucky
The Bender CG&E No. 1 (#139) well is located in Boone County on the margin between the Lexington Platform and the Utica/Point Pleasant sub-basin (Figure 5-1). This well is approximately 25 mi southwest of the Sky Valley well and 40 mi from the Howerton well. There were many aspects of this core that made it difficult to collect good data and perform accurate correlations. Prior to scanning, a significant portion of this core needed to be organized, depth-checked and oriented correctly. Various intervals of this core were missing, most notably the bentonite beds (Millbrig and Diecke) in the Black River. Once the core was organized, it was scanned with surprisingly good results. The core scan matched well with the downhole logs, which include the bentonite marker beds, allowing for a reasonable correlation to the Ohio Howerton core scan. The best correlation was made using the URAN curve and to a lesser extent the GR, POTA and THOR curves. Even so, potassium was still the most influential element with respect to increasing GR readings. The scanned core data were merged with TOC data, which facilitated further data analysis.
The M. Burchell well (#209) is located in Montgomery County, farther south on the Lexington Platform (Figure 5-1). The SGR scan produced reasonable data because the core is in great condition, has good depth markings, and is largely intact. After creating the LAS file and adding TOC data, a reasonable correlation was made with the Bender well, which is about 75 mi to the northwest of the Burchell well. The intensity of GR in this core seemed to be affected mostly by potassium and, in some instances, uranium above the Kope. The TOC relationships are discussed further below.
5.1.4.2 Ohio
All but one of the Ohio cores containing Late Ordovician shale were located in the western half of the state. The Fred Barth No. 3 (#3003; Figure 5-1) is that exception, located in Coshocton County, just west of current Utica drilling activity. The Ohio cores were selected for scanning based on availability of additional data (e.g., TOC, wireline logs), location regarding facies and overall condition, which ultimately facilitated the correlation of these wells across the basin. There are two scans from cores in Butler County, two from Clermont, one from Coshocton, one from Highland, one from Marion and one from Scioto.
The Butler County wells were mainly chosen based mainly on their locations in the Utica/Point Pleasant sub-basin, close to the eastern edge of the "Sebree Trough". The "Sebree Trough" is a narrow northeast-southwest-trending feature described by many as a clastic-filled depression, extending from western Kentucky through southeast Indiana into northwestern Ohio (Patchen and others, 2006). Both cores are relatively shallow and include only the Kope Formation. Core from the Valentine Apple well (#860) is in fair to good condition, but is missing intervals and showed inconsistent depth markings. In spite of this, a realistic LAS file was prepared.
SGR data showed that a majority of the radioactivity was predominantly driven by the percentage of potassium in the Valentine Apple well.
However, there were multiple intervals with more than 10 parts per million (ppm) thorium and uranium, which slightly increased GR readings.
Interestingly, the uranium and thorium spikes were cyclical and offset from one another. As uranium increased, thorium would decrease to zero and vice versa.
The second Butler County core (the Todhunter well, #3446) was chosen as a supplement to the Valentine Apple because they are situated only 900 ft apart. Core from this location is in poor condition and was very difficult to scan. There were missing intervals, varying volumes, and inconsistent depth markers, making it nearly impossible to synchronize with the scanner. An LAS file was created, but the accuracy of the data is suspect. In an attempt to salvage this scan, additional correlations and edits were made, but with little success.
Two cores near the Ohio River in Clermont County were selected for scanning, aiding in the correlation with the southern region of the Study area. These Clermont wells, the Howerton (#2535) and Sky Valley Rec Club (#2536), were drilled by ODGS as stratigraphic tests in the early 1980s, and cores cut at these locations are continuous from the Point Pleasant down to the Black River Formation. They straddle the margin between the Lexington Platform and the Utica/Point Pleasant sub-basin (Figure 5-1). This margin line is somewhat tenuous but is based on the overall thickness of the Trenton Limestone (Patchen and others, 2006).
Both cores were in excellent condition and provide a high confidence level in the SGR scans. Each scan started in the Black River, logging multiple bentonite beds (the Millbrig and the Diecke; see Figure 3-1), which provided good stratigraphic markers. The Sky Valley Rec Club well, located on the sub-basin side of the margin, was scanned first and had intriguingly low (near-zero) GR readings throughout the entirety of the log. Little variation in log readings made it difficult to interpret and correlate, but the scan appeared to be accurate when checked against known calibration standards. The scan also was compared to photographs and core descriptions, further confirming the data that indicate a good correlation between GR and increased shale percentage in the Point Pleasant. The scan revealed that the increase of GR in the Point Pleasant was a direct result of the increased potassium percentage.
Scans from the Howerton well, located on the Lexington Platform side of the margin, had considerably different results, showing higher levels of radioactivity and a notable increase of uranium levels in the upper Lexington. Considering that these wells are only 20 mi apart, similar results were expected. This difference in scan data was investigated further by comparing the rocks in cores from these two wells. Overall these cores are very similar, with the only noticeable exceptions being the nearly missing Point Pleasant and the thinner, less radioactively-intense bentonite beds in the Howerton core.
SGR data from the Howerton well were driven mostly by the percentage of potassium, considering that less than five ppm uranium or thorium were detected until the scan reached the upper portions of the upper Lexington/Trenton Formation. In this member, the most uranium detected was just over 10 ppm, but this did not cause a significant change in GR readings. Samples were taken from this core for TOC analyses, which are included in the LAS for this location.
Thirty miles to the northeast of the Howerton well, in Highland County, the J. Goins well (#2626) was selected due to its pristine condition and paleogeographic location in the Utica/Point Pleasant sub-basin (Figure 5-1). There were few to no missing intervals, and the core had not been excessively split or sampled. The LAS file from the scan was compared to the downhole log and matched almost identically. The natural radioactivity occurring in this well is almost 100% from potassium percentage (Appendix 5-A). There are two small uranium-dominant horizons in the Kope but nothing more. Further data were collected for this well, resulting in a RHOB scan. The smaller diameter of this core presented a unique problem in gathering RHOB data. In order for the scanner to detect a change in density, the core had to be elevated on risers allowing it to sit closer to the cesium source. Overall, the scanned data from this well correlated very well with the nearby Clermont County wells. Core from this well differed in that it included the entire Point Pleasant and Kope intervals, which are not present in either Clermont County core. Samples were taken for TOC analyses, which were studied alongside the spectral/density log.
The Aristech well (#3409) is located approximately 50 mi to the southeast of the J. Goins well on the Lexington Platform (Figure 5-1). This core was in very good condition with few splits or missing pieces, consistent depth markings, and an abundance of supplemental data, including TOC and wireline logs that can be used for evaluation. The LAS file from the scanned core was merged to the downhole LAS file. This merge clearly illustrated that the core scan was about seven feet shallower than the downhole log. This discrepancy is probably caused from mislabeled depths during collection or re-boxing. The original scan depths were maintained when adding the TOC data. Even though this well is located on the Lexington Platform, it encountered about 120 ft of Point Pleasant Formation. Once again, potassium and thorium were the main elements responsible for the increase measure of GR. There were no specific radioactive beds in this core that could be directly linked to an increase in uranium. The uranium content in this core was never measured above six ppm and hardly measured above three ppm. On the other hand, this well displayed some high levels of thorium, with multiple beds measuring contents of 30 ppm or higher. Additional evaluations were completed and are discussed in Section 5.1.5 below.
The Fred Barth No. 3 (#3003) is located approximately 130 mi north of the Aristech well in Coshocton County near the center of the Utica/Point Pleasant basin (Figure 5-1). This core did not produce good SGR results due to its poor condition from over-sampling and missing intervals; approximately 50% of this core was missing when it was donated to the state. Attempts were made to scan the core and correct for missing intervals and changes in volume but with little success. These attempts were made because this is the only core available for study in eastern Ohio close to the current drilling activity. No useful SGR log data have been generated, but photographs were taken to illustrate the organic-rich intervals in this core.
The Prudential well (#3372) is located in Marion County in the northern portion of the "Sebree Trough" (Figure 5-1). This core was a good candidate for SGR scanning because it is a solid core and has modern wireline logs, TOC, X-ray Diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and source rock analysis data. Overall, the scan was successful, but there were some concerns regarding depth, likely due to original mislabeling during core collection and re-boxing. The mislabeled depths resulted in a 20-ft discrepancy between the core scan and downhole logs. As with the previous wells, the GR levels from this core were produced from the increased levels of potassium. Many beds had greater than 30 ppm thorium, and several had uranium levels slightly above 10 ppm, but neither uranium nor thorium caused significant percentage increase in GR. A major problem was still present regarding the TOC data for this well. Even with an understanding of the log discrepancies, there is no way of knowing which depths were used by the five clients who sampled this well for TOC. Therefore, the scanned data cannot be definitively matched with the TOC analyses performed for this well.
5.1.4.3 West Virginia
The Power Oil well (#768) is located in Wood County in the southeast portion of the Utica/Point Pleasant sub-basin (Figure 5-1).
Even though the Utica/Point Pleasant interval in this well is thinner than noted in the Aristech well, which is located on the Platform, it is considered to be located in the sub-basin due to the thinning of the overall Lexington/Trenton Formation.
The data collected for this well were inconsistent because only a ⅓ slab of the core was available and sections were missing, which challenged the scanner capabilities.
The data were converted into an LAS file and merged with the borehole geophysical LAS log and TOC data. Due to missing intervals in the Black River, finding good stratigraphic markers required extensive data manipulation.
After several attempts to correct for the missing intervals and inconsistencies, we determined that further data manipulation would not be beneficial for this Study.
Consequently, the scanned data were left in their original state, which revealed that the potassium percentage was still the most influential element to GR (Appendix 5-A  (PDF, 77 MB; 131 pages)).
(PDF, 77 MB; 131 pages)).
The Lost River cores (#254 and #256) were drilled in 1977 as a part of the Potomac River Watershed Project, Floodwater Retarding Dam No. 27, and are located in the Central Appalachian basin near the Taconic Foredeep (Figure 5-1).
Both cores include the Martinsburg Formation (Utica equivalent in part), are less than 100 ft in length, and are in very good condition.
The scans were successful in gathering SGR data, but the short length and small shale volume limited their use.
No additional data were available for these core locations.
5.1.4.4 New York
The New York Mineral test well (#74NY5) is located in Herkimer County in a deeper-water environment east of the carbonate platform (Figure 5-1).
This slabbed core is in excellent condition with no missing intervals, which allowed for the collection of very good data.
Overall, the GR was evenly influenced by potassium and uranium with very little amounts of thorium.
The relationship, albeit weak, between URAN and GR for this well was not seen in any other well scanned for this task and may be a result of deeper-water deposition.
The TOC data were added to the scan and additional correlations were made with Ohio, West Virginia and Kentucky core data.
5.1.5 Discussion
5.1.5.1 Overview
The GR log was the first nuclear well log used in industry and was introduced in the late 1930s (Schlumberger, 1997).
This log measures natural radioactivity in API units, and is generally used as a correlation tool.
The natural radioactivity in rocks comes from any of three elemental sources, uranium, potassium and/or thorium.
Each element emits unique gamma rays with characteristic energy levels that can be measured using a scintillation detector.
Knowing the amount of each element in a rock can help determine several features, but only depositional environment and TOC are discussed here.
Knowing the origins of these elements and how they react in different environments is essential in determining depositional history.
Uranium-238, the most common isotope of uranium, is naturally occurring in seawater at around three parts per billion (ppb).
Disseminated uranium dioxides precipitate out of the seawater onto organic matter by forming organometallic complexes at the sediment-water interface under anoxic conditions (Swanson, 1960; Lunig and Kolonic, 2003).
This implies that rocks with high uranium content may have been slowly deposited in anoxic conditions, allowing for extended time at the sediment-water interface, and consequently may be associated with elevated levels of organic carbon.
In contrast, potassium and thorium do not occur naturally in seawater but are transported there for deposition.
Potassium is most commonly found in clays or potassium feldspars. The clay materials associated with potassium are illites and smectites, which are chemically weathered from a parent material.
Thick deposits of clays generally are a result of terrigenous, pelagic or hemipelagic deposition (Bohacs, 1998; Boggs, 2006).
Potassium-rich clays are generally not associated with organic matter, but they may amalgamate and can be deposited simultaneously in lower-energy waters.
Thorium is often associated with heavy minerals, such as sulfides, oxides and some silicates.
These usually originate and weather from igneous parent material and are typically deposited in beach or alluvial environments, sometimes referred to as heavy-mineral placers (Boggs, 2006).
Such environments are higher-energy settings that are generally oxygenated.
Because organic matter is subject to oxidation and bacterial decomposition, it is unlikely that thorium and organic carbon would be concurrently deposited.
5.1.5.2 Correlations
The compiled dataset, including all SGR core scans, TOC data and downhole geophysical logs, was standardized and imported into the Landmark GeoGraphix® software for further evaluation.
Crossplots were generated to analyze the correlations of multiple aspects, including: (1) core scan versus downhole SGR logs;
2) prevalent radioactivity; (3) TOC versus GR, URAN, POTA or THOR; and (4) whether relationships vary among the different facies deposited during Lexington/Trenton-to-Point Pleasant time.
All correlation coefficients are provided in Table 5-2, and all crossplots are included in Appendix 5-A.
Correlations assessed linear trends and refer to a correlation coefficient 'r', the classification of which is as follows:
- 0.8 to 1.0 or -0.8 to -1.0 (very strong relationship)
- 0.6 to 0.8 or -0.6 to -0.8 (strong relationship)
- 0.4 to 0.6 or -0.4 to -0.6 (moderate relationship)
- 0.2 to 0.4 or -0.2 to -0.4 (weak relationship)
- 0.0 to 0.2 or -0.0 to -0.2 (no relationship)
| Well Name | GR vs
POTA | GR vs
URAN | GR vs
THOR | GR vs
KTh | TOC vs
GR | TOC vs
POTA | TOC vs
URAN | TOC vs
THOR | TOC vs
RHOB |
|---|
| All Wells in Study* | 0.588 | 0.285 | 0.447 | 0.981 | -0.008 | -0.251 | 0.101 | 0.122 | -0.304 |
All Core Data
(Scanned Core) | 0.631 | 0.307 | 0.201 | 0.982 | -0.014 | -0.260 | 0.098 | 0.126 | -0.363 |
Active Area
(Eastern OH, Northwestern PA)* | 0.879 | 0.597 | 0.889 | 0.961 | -0.099 | -0.266 | 0.238 | 0.201 | -0.295 |
Inactive Area
(Western OH, KY, NY, PA, and WV)* | 0.597 | 0.253 | 0.334 | 0.998 | 0.117 | -0.246 | -0.141 | -0.116 | -0.252 |
| Bender_KY139 | 0.483 | 0.106 | 0.185 | 0.995 | 0.250 | 0.255 | -0.144 | 0.041 | Null |
| Burchell_KY209 | 0.464 | 0.308 | 0.065 | 0.993 | -0.424 | -0.267 | -0.069 | 0.201 | Null |
| Aristech_OH3409 | 0.853 | 0.454 | 0.377 | 0.999 | -0.441 | -0.384 | -0.149 | -0.137 | 0.092 |
| Power Oil_OH768 | 0.667 | 0.126 | 0.078 | 0.999 | -0.280 | -0.335 | 0.019 | -0.195 | Null |
| Mineral_NY74-NY-5 | 0.250 | 0.231 | 0.055 | 0.987 | 0.441 | -0.153 | -0.029 | -0.013 | Null |
Hershberger
Devon Data* | 0.978 | 0.957 | 0.972 | 0.980 | -0.164 | -0.199 | -0.128 | -0.221 | -0.714 |
Chumney Family
Devon Data* | 0.976 | 0.865 | 0.967 | 0.981 | -0.214 | -0.328 | 0.033 | -0.273 | -0.629 |
Richman Farms
Devon Data* | 0.976 | 0.946 | 0.963 | 0.979 | -0.019 | -0.070 | 0.069 | 0.074 | -0.734 |
Georgetown Marine_OH5073
(Sample)* | 0.944 | 0.249 | 0.908 | 0.954 | -0.345 | -0.282 | -0.133 | -0.567 | 0.317 |
| Howerton_OH2535 | 0.626 | 0.271 | 0.124 | 0.995 | -0.372 | -0.161 | 0.001 | -0.151 | Null |
| J.Goins_OH2626 | 0.744 | 0.313 | 0.134 | 0.998 | -0.231 | -0.377 | 0.416 | 0.231 | Null |
Mull Edith_OH3890
(Sample)* | Null | Null | Null | Null | 0.317 | Null | Null | Null | -0.432 |
| Prudential_OH3372 | 0.89 | 0.427 | 0.289 | 0.999 | -0.579 | -0.523 | -0.283 | -0.268 | Null |
Table 5-2. Correlation coefficients for each crossplot of GR, POTA, URAN, THOR, KTH, TOC and RHOB. * denotes wells that have density crossplots.
The first step in our evaluation was to assess the relationship between the SGR core scans generated by the SGL-300 and the downhole SGR logs. The most notable difference between these is the total GR curves. The SGL-300 produces very consistent results because it was calibrated to the same set of standards at a constant gain setting on a daily basis, whereas the downhole logs were collected by different companies using different standards that are calibrated at various gain settings. The gain setting simply increases or decreases the amplitude of the GR signal. The SGL-300 gain is consistently lower than most downhole logs, but the overall signals are the same. Another difference, which is thought to be a product of scintillator resolution, is how well the radioactive elements are recorded. The SGL-300 uses a high-resolution scintillator that easily differentiates the radioactive gamma characteristics of URAN, POTA and THOR, whereas the scintillators on downhole wireline tools are not as good at separating the unique gamma signals. This is best observed when comparing the GR/POTA, GR/URAN and GR/THOR crossplots from any core scans to the same crossplots from a downhole well log.
The best radioactive correlations from core scans are GR/POTA, which tend to show a strong to very strong relationship, whereas THOR and URAN show a weak to no relationship. Compared to the same GR/POTA, GR/URAN and GR/THOR crossplot correlations from downhole logs, all but one correlation is very strong. These differences need to be considered when using SGR data for further analysis.
Acknowledging that core scans and downhole logs vary in resolution was important when determining which radioactive element was generating GR variations. For this part of our work, only data from the core scans were used. A multi-well analysis on the entire basin demonstrated a decreasing strength in relationship to GR from POTA to URAN to THOR. The POTA had the most consistent influence on GR with an overall core data r-value of 0.631, indicating a strong relationship. This relationship did vary among facies; the strongest occurred in the Utica/Point Pleasant sub-basin, on the Lexington Platform margin, and in the "Sebree Trough". The Prudential well in the northern portion of the "Sebree Trough" had the strongest GR/POTA relationship with an r-value of 0.890. This is likely due to the increased water depth and decreased energy in the sub-basin and trough. The weakest GR/POTA relationships occurred farther down on the Lexington Platform and in New York. The Burchell well in Kentucky had a moderate relationship (r = 0.464), and the New York core had a weak relationship (r = 0.250). The weaker relationship on the Lexington Platform is likely due to increased energy and carbonate percentage. The very low GR/POTA relationship in the New York core is different altogether and may be a result of its clastic source, which is unique to this location.
The basin-wide GR/URAN core data multi-well relationship, although not as significant as GR/POTA, is still interesting. Of the three radioactive elements, uranium has the highest weight percentage influence on the total GR, allowing very small amounts to influence total radioactivity. This could be a factor in the overall weak GR/URAN relationship (r = 0.307) in Upper Ordovician shales. The statistical relationship varies from almost nil (r = 0.126) in the Power Oil well to moderate (r = 0.427) in the Prudential well. There are no prevailing trends among the different facies, but we argue that the deeper, less-oxygenated water in the “Sebree Trough” may play a role in statistical relationships we observed.
The last radioactive element that influences GR is thorium. Based on the results of our work, however, thorium does not play a significant role. This is evidenced by the very weak relationship (r = 0.201) exhibited by our multi-well analysis of core data. Further, most wells evaluated in this task, with the exception of the Prudential, show no relationship, with r-values ranging from 0.055 to 0.134. The Prudential well has a weak GR/THOR relationship (r = 0.289). This may be due to a few beds with higher levels of thorium, but as a rule, only very minor amounts of thorium are present.
5.1.5.3 Relationships with TOC
Initially, all well data collected as part of this task were evaluated together to determine whether a relationship exists between Utica and equivalent GR signatures and TOC,
but this approach provided unexpectedly poor results (Figure 5-2). The multi-well regression produced an r-value of -0.008. In addition to the lack of correlation, the regression line is negative.
Generally, we would expect to see TOC increase along with GR. Investigating further, an analysis utilizing only the high-resolution core data still showed no correlation between GR and TOC (r = -0.014).
The last evaluation of a potential multi-well GR/TOC relationship used data near the active drilling portion of the play, which includes eastern Ohio counties and northwestern Pennsylvania.
Again, a negative correlation was derived (r = -0.099). In fact, there was a weak to no relationship for GR/TOC for all but four wells evaluated in this task.
These wells (i.e., the Burchell, Mineral, Aristech and Prudential) displayed a moderate relationship.
At this point, the Prudential well was eliminated from consideration due to its questionable core depths.
Of the three remaining wells with a moderate GR/TOC relationship, only one had a positive correlation – the New York Mineral Core (r = 0.440).
This could be a result of deposition of uranium and organic matter in deeper waters.
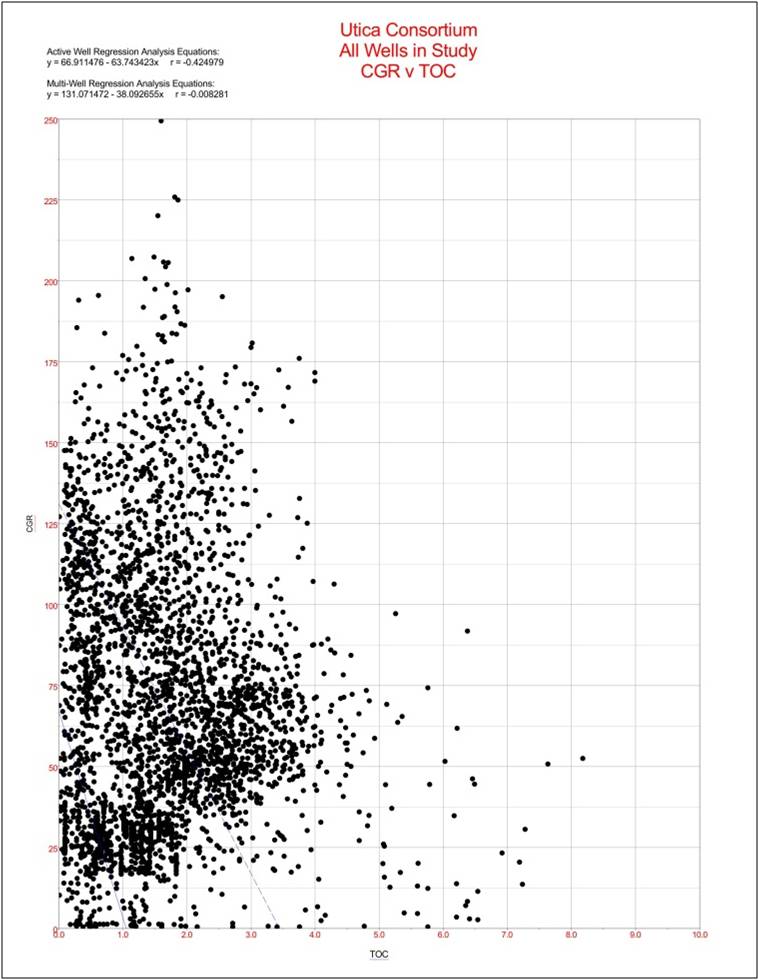
Figure 5-2. Correlation crossplot for core gamma-ray (CGR) and TOC using all wells in the Study.
Considering the GR signature is a composite of three radioactive elements, and no significant relationship was observed between GR and TOC,
little correlation was expected when evaluating the relationship of TOC to POTA, URAN or THOR. The overall POTA/TOC relationship was weak (r = -0.251), when using the entire well dataset.
An encouraging aspect was the negative regression, which made sense considering potassium has no real depositional relationship to TOC.
The relationship was consistently weak even when evaluating only core data, active/inactive drilling areas, facies changes and each formation.
Correlations were made for individual wells and varied from no relationship at the Richman Farms well (r = -0.070) to a weak relationship in the Aristech well (r = -0.384).
The URAN/TOC relationship also was weak to nonexistent.
The multi-well analysis using all data collected for this task had no relationship (r = 0.101).
Similar to the POTA/TOC relationships, no matter how it was tested, the URAN/TOC relationship produced r-values of 0.001 to 0.237.
One weak relationship (r = 0.237) came from the active drilling area test.
An anomalously high relationship of r = 0.416 was observed from the J. Goins well, indicating a moderate relationship, but this was considered to be an artifact of having too few data points.
The last radioactive element potentially related to TOC was thorium.
Little relationship was expected between the two, and the results of our evaluation confirmed this.
Using all the wells in the dataset, we observed no relationship (r = 0.122).
In fact, only one well (the Georgetown Marine well, which is located in Belmont County, Ohio) showed a moderate relationship.
Like the J. Goins anomaly noted above, we have interpreted the relationship reported for the Georgetown Marine well to be a result of a limited dataset.
This work has demonstrated that GR/TOC and/or URAN/TOC relationships only develop in certain shale systems, and the Utica/Point Pleasant system in the Appalachian basin is not one of them.
This may be due in part to the high percentage of carbonate present in these rocks. The Utica is described as containing 20% carbonate and the Point Pleasant 60% (Schumacher and others, 2013).
Another reason could be position of the redox boundary relative to the sediment-water interface and/or length of depositional anoxic conditions.
A number of factors could play a role in the weak relationships of GR, POTA, URAN and THOR to TOC, but suffice to say, none of these support the creation of a proxy for predicting TOC in the Utica Shale play.
5.1.6 RHOB to TOC
Although not part of the original SGR core scanning task, we have investigated the potential relationship of RHOB to TOC, given the disappointing findings of our SGR/TOC statistical evaluations.
Bulk density relates to TOC because of the low grain density of organic matter, which can range from 0.95 to 1.6 grams/cubic centimeter (g/cm3).
These are much lower than typical mineral grain densities, which typically vary from 2.5 to 3.0 g/cm3.
The relationship is not constant, however, and can vary greatly with both organic type (Type II vs. Type III) and thermal maturity (Cluff and Holmes, 2013).
Other variables that must be considered are amounts of pyrite, formation porosity and mass of organic carbon (Schmoker, 1993).
The following are examples gathered in this study to show both the possibility and inconsistency, illustrating the localized analysis that needs to be done when predicting TOC.
When using all well data for this analysis, RHOB/TOC exhibits a weak relationship (r = -0.304).
However, when evaluating individual wells, much better relationships were observed.
The best example comes from the Richman Farms well (Medina County, Ohio), which showed a strong RHOB/TOC relationship (r = -0.734).
Other well correlations confirm this relationship and are included in (Appendix 5-A  (PDF, 77 MB; 131 pages).
(PDF, 77 MB; 131 pages).
5.1.7 Summary and Conclusions
During shale deposition, several factors play important roles in the preservation of radioactive elements and organic matter.
The presence of potassium, uranium and thorium in shales can help determine the depositional environment(s) for the unit, as well as the likelihood that organic matter will be deposited.
A good example of this is the Devonian Marcellus Shale, which has a good correlation among GR, uranium signature and TOC measurements (Cluff and Holmes, 2013).
Unfortunately, the Upper Ordovician shales in the Appalachian basin do not exhibit this same relationship.
The GR intensity for Utica and equivalent rocks is dominated by the presence of potassium, and there is no correlation with the amount of organic matter.
Factors that may prevent such a relationship include, but are not limited to, the influence of carbonate material, the lack of available uranium in seawater, or the amount of oxygen in the system.
This investigation clearly demonstrates that TOC does not directly correlate to any radioactive material in the Utica/Point Pleasant interval.
Other methods may be better gauges for predicting TOC in the Ordovician shales, such as bulk density and/or the ∆log R method (see Meyer and Nederlof, 1984; Passey and others, 1990; and Herron, 1991).